What are Microgrids? An In-Depth Look

As the global community grows increasingly focused on sustainable and reliable energy solutions, the concept of the microgrid has emerged as a topic of significant interest. But what exactly is a microgrid? In this post, we will delve into the intricacies of microgrids, exploring their structure, benefits, and potential role in shaping our energy future.
What are Microgrids
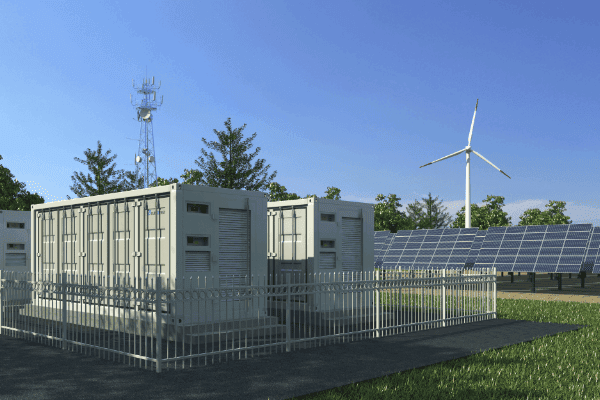
At its most basic, a microgrid can be defined as a local energy system capable of operating autonomously or in conjunction with the main power grid. Typically, it encompasses a variety of distributed energy resources (such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems) and loads (consumers of energy). These resources and loads are managed in a coordinated fashion to ensure efficient and reliable power delivery within a specific geographic area.
Key Features of Microgrids
- Autonomy: One of the most distinguishing features of a microgrid is its ability to ‘island’ itself. This means that in situations where the main power grid may experience disruptions or outages, a microgrid can continue to operate independently, ensuring continuous power supply to its users.
- Diverse Energy Resources: Microgrids often incorporate a mix of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, alongside traditional generators and energy storage systems. This diversified energy mix not only promotes sustainability but also aids in maintaining energy supply during variable conditions.
- Advanced Control Systems: Modern microgrids are equipped with sophisticated control systems that can optimize energy production, storage, and consumption in real-time, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
Benefits of Microgrids
- Resilience: Given their ability to operate autonomously, microgrids can provide power during main grid outages, acting as a backup and increasing resilience against blackouts or natural disasters.
- Sustainability: With an increasing reliance on renewable energy sources, microgrids can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a more sustainable energy landscape.
- Economic Savings: By optimizing energy production and consumption, microgrids can lead to cost savings for end-users and allow participation in demand response programs, providing further economic incentives.
- Grid Support: Microgrids can offer services like voltage support, frequency regulation, and reactive power to the main grid, aiding in maintaining its stability and reliability.
Challenges and Considerations
While microgrids present numerous advantages, they are not without challenges. Integrating various energy resources requires advanced management systems. Ensuring cybersecurity, funding the initial setup, and navigating regulatory landscapes are some of the hurdles to widespread microgrid adoption.
The Future of Microgrids
With advancements in technology and a global push towards sustainable energy solutions, the role of microgrids is expected to grow significantly. They can be particularly valuable in remote locations, where extending the main grid might be impractical. Furthermore, as urban areas become more focused on achieving energy independence and resilience, the incorporation of microgrids in city planning and infrastructure development is likely to increase.
Microgrids, with their ability to integrate diverse energy sources and offer both autonomy and efficiency, represent a promising avenue for the future of energy systems. As the world seeks more resilient, sustainable, and localized energy solutions, understanding and leveraging the potential of microgrids will be paramount. As with any technological advancement, challenges exist, but with continued research and investment, microgrids stand poised to play a pivotal role in our energy future.